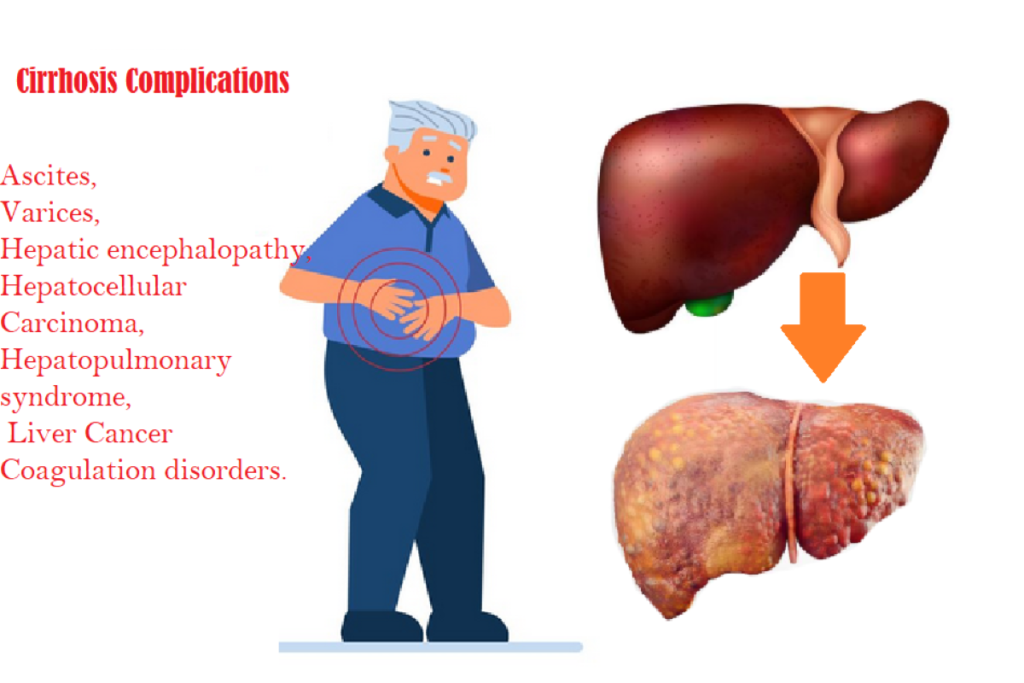
Overview Of Cirrhosis Complications
Cirrhosis is a condition resulting from long-term liver disease, in which the liver becomes permanently damaged. According to top rated liver transplant hospitals and liver surgeons, cirrhosis develops slowly over many years due to various reasons, with alcohol, drugs, viruses, and metabolic factors being majorly involved. These damage healthy liver tissue and cause permanent lesions on the liver. Eventually, your liver may stop functioning properly. Liver cirrhosis and its associated issues are portal hypertension, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal syndrome, insulin resistance, and diabetes. To put it simply, the complications of cirrhosis affect multiple organ systems in your body.
Additionally, cirrhosis increases the risk of liver cancer and may impair blood clotting. Cirrhosis cannot be completely cured, but our liver treatment doctor believes that early diagnosis and treatment can be an important option to prevent cirrhosis-related complications, which can stop its progression or delay its development. In this blog, we will discuss what complications arise from cirrhosis, and how can they be managed?
What Are The Cirrhosis Complications?
It usually takes several years for liver damage to progress to cirrhosis, in which normal liver tissue gradually turns into lifeless (hard) scar tissue. As cirrhosis gets worse, there will be less healthy normal tissue in the liver and, as a result, the flow of blood and oxygen may be blocked, causing your liver to lose its ability to process blood, metabolize nutrients, and filter out toxins. However, a liver expert doctor at Dr L H Hiranandani Hospital explains that there are often no symptoms until cirrhosis complications become severe, and when symptoms do arise, liver cirrhosis and its associated issues, ranging from portal hypertension, ascites to hepatic failure, can be detected. In addition, other various cirrhosis complications may include encephalopathy or liver cancer, varices, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatopulmonary syndrome, and coagulation disorders.
Portal Hypertension
Portal hypertension is a serious complication of cirrhosis in which there is abnormally high blood pressure in the portal vein. According to our liver surgeons, the portal vein carries blood from the intestine to the liver, but damaged tissue due to thrombosis narrows these passing blood vessels and reduces their blood flow. Due to this, many other organs of your body are more likely to be affected, and in severe cases, it can cause internal bleeding and other problems.
Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological intervention can be done to reduce high portal blood pressure, although drugs like beta-blockers, vasopressin, or octreotide are the treatment of choice by a top liver transplant surgeon in India in severe cases of bleeding from esophageal varices.
Endoscopic Procedures
Endoscopic procedures are performed to treat high portal blood pressure. Through this procedure, the liver treatment doctor and his team can confirm whether new collateral veins have developed in the liver due to internal bleeding, inflammation, or high blood pressure in the case of portal hypertension. For this, liver surgeons usually use a flexible viewing tube (endoscope).
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (Tips)
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a procedure performed to reduce portal blood pressure or redirect blood flow. In which the portal vein or one of its branches can be connected to a vein of the general circulation. The best liver transplant specialist in India can perform various portosystemic shunt procedures depending on the individual’s case, one of which includes the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedure in the case of portal hypertension type. During this procedure, a liver expert doctor will take X-rays or CT scaning. To help find the way inside the veins, a catheter with a needle is inserted into a vein in the neck and connected to the hepatic veins.
Ascites
Top rated liver transplant hospitals commonly treat ascites as a major complication of cirrhosis, which is defined as the presence of excessive fluid in the peritoneal cavity. Portal hypertension is the main factor, apart from this, other reasons like chronic hepatitis C or B infection, and excessive consumption of alcohol for many years can also be included. Our liver surgeons explain that in the case of cirrhosis when the pressure in the vein that supplies blood to the liver increases, the increased pressure can cause fluid to accumulate in the space between the stomach lining and the abdominal organs, which is called ascites. However, other diseases can also cause ascites which can cause serious liver damage.
Dr L H Hiranandani Hospital offers the fastest and most cost-effective methods of treatment, such as sodium restriction, diuretic therapy, and paracentesis as treatment options for cirrhosis complications such as ascites. Additionally, our advanced radiographic techniques are useful in defining the extent of ascites in your new onset or worsening ascites.
Sodium Restriction
Sodium restriction is a fundamental aspect of the management of ascites in cirrhosis. Sodium restriction of 2000 mg per day is usually recommended by a liver treatment doctor, as limiting sodium intake or following a low-sodium diet helps reduce fluid retention in the body, thereby reducing the severity of ascites.
Diuretic Therapy
Diuretic therapy is often prescribed by your liver expert doctor to increase fluid elimination from your body and reduce ascites. Medications such as spironolactone and furosemide are commonly used to increase urine output and reduce fluid retention. The best liver transplant centers in India primarily use diuretic therapy in the management of ascites improving outcomes in cirrhosis management. It intends to reduce fluid buildup and alleviate symptoms. However, it is important to closely monitor electrolyte levels and kidney function during this period, as diuretic medications may also have common side effects, which may include hypokalemia, hypochloremic alkalosis, hyponatremia, and hypovolemia.
Paracentesis
Paracentesis is an effective procedure performed to remove excess fluid from the abdominal cavity in cases of severe or refractory ascites. Through a safe procedure, a needle is inserted into the abdomen, and fluid is removed, providing rapid relief from symptoms such as abdominal distension and discomfort. Paracentesis may be recommended by liver surgeons on an as-needed or scheduled basis to manage recurrent ascites.
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is a serious neurological complication of liver disease, causing cognitive dysfunction and altered states of consciousness. According to the best liver transplant specialist at Dr L H Hiranandani Hospital, toxins absorbed into the bloodstream from the intestine are normally removed by the liver. However, due to poor liver function, portal hypertension, or abnormal connections (collateral vessels) that form between the general circulation and the body, toxins (such as ammonia) bypass the liver and reach the brain directly, impairing brain function. Although liver surgeons are not sure exactly which substances are responsible for affecting the brain, toxin exposure to the brain can cause several mental problems, including decreased alertness and confusion, as well as cognitive impairment in the early stages. It also includes loss of thinking. For the prevention of cirrhosis-related complications, like in Hepatic encephalopathy, we provide lactulose and rifaximin therapy, dietary protein restriction, or effective management of precipitating factors aimed at reducing ammonia levels in the body and resolving precipitating factors.
Lactulose And Rifaximin Therapy
Treatment typically involves the use of lactulose, a non-absorbable sugar that promotes ammonia excretion in the stool, and rifaximin, an antibiotic that reduces ammonia-producing bacteria in the intestines. This combination of therapy helps reduce symptoms and prevent recurrent episodes of hepatic encephalopathy.
Dietary Protein Restriction
Dietary protein restriction may be recommended to reduce ammonia production in the intestine. Limiting protein intake helps reduce ammonia levels in the bloodstream, which improves symptoms and reduces the risk of hepatic encephalopathy episodes.
Management Of Precipitating Factors
Management of hepatic encephalopathy requires identifying and addressing precipitating factors such as infection, electrolyte imbalance, gastrointestinal bleeding, and drug toxicity. Prompt intervention and comprehensive management of these factors are important to prevent worsening of symptoms and improve outcomes.
Hepatorenal Syndrome
Hepatorenal syndrome is a serious complication of advanced liver disease, characterized by renal dysfunction and impaired renal function. Treatment options aim to improve renal perfusion and prevent further kidney damage.
Intravenous Albumin Administration
Intravenous albumin administration is the cornerstone of the treatment of hepatorenal syndrome. Albumin infusion helps improve renal perfusion and intravascular volume, thereby improving kidney function and reducing the risk of kidney failure.
Vasoconstrictor Therapy
Vasoconstrictor therapy, often in combination with albumin administration, helps to improve renal blood flow and systemic circulation. Medications such as terlipressin or midodrine can be used to increase vascular tone and renal perfusion, thereby reducing hepatorenal syndrome.
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplant treatment is the only last resort for hepatorenal syndrome. By replacing the diseased liver with a healthy donor liver through liver transplant surgery, liver transplantation resolves the underlying liver dysfunction and often leads to improvement or resolution of hepatorenal syndrome. However, according to top rated liver transplant hospitals, transplantation may not be possible for all patients and requires careful evaluation and consideration of individual factors by liver surgeons.
Coagulopathy
Coagulopathy in cirrhosis complications refers to poor blood clotting, often seen in liver disease due to decreased synthesis of clotting factors. Managing the risk of bleeding and management strategies such as vitamin supplementation, transfusion of blood products, or medication adjustments to improve clotting function may be important in preventing these types of cirrhosis-related complications.
Vitamin K Supplementation
Vitamin K supplementation is often recommended by the liver treatment doctor to promote the synthesis of clotting factors in the liver, thereby helping to restore normal coagulation function.
Transfusion Of Blood Products
Transfusion of blood products, such as fresh frozen plasma or platelets, is commonly used by liver surgeons to compensate for the lack of blood clotting factors and prevent bleeding complications in patients with severe coagulopathy.
Medication Adjustments
Liver transplant hospitals often incorporate ratio-based transfusion therapy as an effective option to reduce the risk of bleeding in individuals with coagulopathy. Medication adjustments may be necessary, including dose reduction or discontinuation of anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents.
Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is a complex disease usually caused by the uncontrolled growth of cells in the liver, which destroy and replace liver cells. At the best liver transplant center in India, our renowned liver surgeons understand the intricacies of liver cancer from accurate diagnosis to treatment. In this, we collaborate and work as a multidisciplinary team to provide patients with seamless access to all options, even the most complex cases. It includes comprehensive management strategies to address disease progression and improve patient outcomes in liver cancer, including hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Surveillance With Imaging Studies
Your liver expert doctor may perform regular monitoring using imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI scan for early detection and monitoring of liver cancer. In liver cancer, timely detection leads to early intervention and potentially better treatment outcomes.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions, such as liver resection or liver transplant surgery, can be considered for selected cases of localized liver cancer or advanced liver disease at top rated liver transplant hospitals. Liver transplant treatment aims to replace the cancerous liver with a healthy liver obtained from a suitable donor and to improve long-term survival.
Ablation Therapy
The best liver transplant specialist in India often use ablation therapy techniques like radiofrequency ablation or microwave ablation to destroy the cancerous tissues in the liver. Ablation therapy may be recommended by liver surgeons as a suitable option primarily in cases where surgery is not possible or in cases such as small tumors.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is used to target cancer cells and stop tumor growth. Chemotherapy drugs may be given orally, intravenously, or directly to the tumor site.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies targeting molecular pathways involved in cancer development and progression can be used alone or in combination with other therapies to improve outcomes in the liver.
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is a common concern in people with liver disease or liver cirrhosis and its associated issues. The Liver expert doctor explains that impaired liver function results in impaired metabolism of nutrients, hence specific interventions are required to correct nutritional deficiencies and improve overall health.
Nutritional Support
Nutritional support, including enteral or parenteral nutrition, may be necessary to ensure adequate nutrient intake and prevent malnutrition in patients with liver disease or other cirrhosis complications.
Dietary Counseling
Dietary counseling by health care professionals, such as a liver hospital or liver expert doctor, helps you optimize nutrition and make informed dietary choices to support liver function.
Oral Supplements
Oral supplements containing essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals may be prescribed to supplement dietary intake to address liver malnutrition during cirrhosis complications.
Insulin Resistance And Diabetes
Insulin resistance and diabetes often co-exist with liver disease or cirrhosis complications, since liver failure harms many internal functions, including the pancreas, which pumps insulin to deliver blood sugar into cells. Insulin also signals the liver to store blood sugar and alerts the liver to release stored blood sugar when levels get low in the bloodstream, so energy is always available. But in the case of insulin resistance and diabetes, too much blood sugar enters the bloodstream, which is very harmful to the body. Targeted management given to optimize glycemic control and reduce associated complications helps in improving outcomes in cirrhosis management.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes, including regular exercise, weight management, and dietary adjustments, can help manage insulin resistance and diabetes in liver cirrhosis and its associated issues.
Oral Antidiabetic Medications
Oral antidiabetic drugs, such as metformin or sulfonylureas, may be prescribed by a liver expert doctor to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity in liver cirrhosis and its associated issues.
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy, including basal or prandial insulin regimens, may be necessary for liver cirrhosis and its associated issues, especially in those who fail to achieve glycemic targets with oral medications alone.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential to track glycemic control in liver cirrhosis and its associated issues and to adjust treatment regimens as needed to prevent hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Cirrhosis presents a spectrum of complications that have a significant impact on the patient’s health and quality of life. These complications include portal hypertension, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal syndrome, coagulopathy, liver cancer, malnutrition, insulin resistance, and diabetes. However, with comprehensive management strategies, these complications can be effectively managed and their impact minimized. Our personalized follow-up plan at Dr L H Hiranandani Hospital helps liver surgeons and their care team to monitor these changes in your liver cirrhosis and its associated issues, including early detection of complications and slowing the progression of cirrhosis patients. Early detection, prompt intervention, and continuous monitoring can potentially improve outcomes and recurrence in cirrhosis management after treatment.